Off the Top: Enterprise Entries
Showing posts: 1-15 of 25 total posts
Weeknote - 25 October 2020
I’m returning back to something I read a bit ago from Matt Webb about getting back into a habit for blogging again. Matt’s posting about 15 rules for blogging, and my current streak is one that really struck home as I’m trying to get back to a regular writing habit, here and elsewhere. Matt’s idea for one idea per post is the old school way of knocking out quick short notes on one topic for reference for one’s self, but also sharing out for others by default. The weeknote model runs a bit counter to this, but trying to get back to a habit of capturing things and trying to get to a schedule helps get things moving again. Matt’s post is more than worth your time.
The week was heavily focussed on the work front as trying doing work that could really benefit from a good innovation space with large whiteboard and to include teammates to think and work through the flows and integrated systems. I’ve been working through a solutions to a gap that makes some easy solutions not viable due to compliance and needing to craft for a large enterprise and the constraints and diversity of needs. The start to the solution came about about 3 weeks ago and trying to work through a solution for one piece of it that would remove a lot of manual work that has a lot of opportunity for error as it scales and scope increases. Getting he foundations right is key, but I think we will have a good solution. Working through permeations of scenarios and modifications coming from vendors was a good chunk of working with large logic puzzles, but the foundation should be good. Now to work on workflows and interactions for it, or at least the first step and a solid system of record for these. I love this type of work, but it is much more sane with a good sized room, large whiteboard and stickynotes, and a few others to work through permeations and potential missing manhole covers that are created when the goal is seeing them and resolving them.
Early voting starts this week and trying to sort out when I can fit that in. While today (Sunday) was eerily quiet, which could be the cold snap or Covid cases spiking at its worst everywhere around the U.S. and people playing safe, I don’t expect that quiet to last for the week.
Read
A really quiet week on the reading front. I have some things to read this next week for a quick review that I am really looking forward to.
Watched
I sort of stumbled onto starting the Finnish crime drama, Deadwind that is on Netflix. I have only watched one episode, but I think I will stick with it. I thought it was a different series, but it has me interested.
One of the things that had me intrigued is not so much the show, but it is in Finnish. I haven’t listened to a lot of Finnish as an adult and its spoken and linguistic patterns are well outside of any language I have a passing understanding of. I was reading the closed captions and trying to pull out some words that could work as way in, but that was tough. I also realized I really liked the cinematography and focussing on closed captions and thinking about language structure was a bit in the way of what had drawn me in.
Listened
Over the past year I’ve become a fan of Rick Beato’s YouTube channel and I stumbled onto his break down of Peter Gabriel’s In Your Eyes in the episode What Makes This Song Great? Ep.27 Peter Gabriel. There is so much more to this song and with Rick had taken another 30 minutes to dig into that.
Productivity
I’ve been using Obsidian more and a release that should hit those with early access and allowing block addressability really looks good. I’m finding with what Obsidian offers I’m able to really get a lot of crosswalks between ideas, sources, authors / creators, and structures that I just didn’t have access to before. Already it feels a bit like I have a James Burke far transfer method in the works that is part of the structure of his Connections series.
Breaking Radio Silence Again
It has been a while since I’ve posted here. I’m thinking I may go back to a daily update for a stretch to keep the blogging muscle limber and trained.
Personal InfoCloud Backlog too
Over on other blog, [http://www.personalinfocloud.com](Personal InfoCloud) I have had a few more recent posts, but I have a very long backlog of content for that space as well. I need to rewrite the intro to the latest post there, [http://www.personalinfocloud.com/blog/2016/6/20/team-roles-needed-for-social-software-projects](Team Roles Needed for Social Software Projects).
I also have a series there called [http://www.personalinfocloud.com/?category=Shift+Happened](Shift Happened) that I have at least 12 most posts that need to get written (edited, or more likely rewritten). The next two in the Shift Happened series are related to UX in enterprise software and services and the subject of Adaption. Both of these subjects could likely have more than one post each. The UX in enterprise needs a grounding / framing piece as many still think of UX as visual design and not things being designed for use (nor all the various roles and domains that make up successful UX design). The Adaption pieces need the framing of complexity and complex adaptive systems to get set as a footing, but also needs to frame how adaption works and enables being comfortable in an ever changing environment that we live in today. As well a focus on Adaptive Road Maps is needed as how one plans in an ever shifting and complex environment is needed when today’s road maps for the next 2 to 5 years are shot to pieces after a quarter or two. Having and maintaining a long focus on where a company or product is headed is really helpful, particularly when needing to understand foundation priorities needed for a long haul in a world were agile practices drive the day-to-day, but those agile practices are incredibly nearsighted and often discourage the long view (I’ve had a lot of work related discussions about this in the last 6 months or so as it is a common deep pain point for many).
Health
A common question is about health after the eColi issue in 2014 to early 2015. My health seems to be good. Getting through last winter’s holiday season had me on edge as I was partially expecting to fall ill again. Thankfully, I stayed healthy.
Inviewed on Shift Podcast
On Friday I had the pleasure of spending about an hour with two of my favorite people, Euan Semple and Megan Murray on the wonderful podcast, Shift. We covered tagging, taxonomies, meaning, power, and the future that we are all hurtling towards.
I am a big fan of their interviews (as their conversations between them are familiar from past conversations between us) with other. I still have a few to get to.
Design and Business Leadership Snippets
There have been quite a few pieces lately on the importance of design and design leadership. The importance of design is getting to the true understanding of what the problems are and thinking about solving out from there without preconceptions of solutions, but letting solutions evolve form the need. Different and well fitting solutions often result from this approach, which is real innovtion and not copying someone else’s solutions for your use as innovation approach.
Matt Milan’s “It’s never been more important for design firms to think differently” is the cornerstone for this thinking differently approach and its deep value. I’d add to this is knowing not only the current state of where the various mediums, systems, and devices are sitting, but where they are headed in the next year or two, so to openly plan for adaption and keep the potential integrations as open possibilities.
Brian Zmijewski’s The Design Leadership Gap and Lead by Design are two really good pieces that take a look at the need for strong design leadership.
Kai Brunner’s Is DevOps Driving the Future of UX Design? is a great look at how to mix and have success with design and DevOps. The two prodominant models don’t really work well and how to work to get to a more optimal model.
KM World 2014 Wrap
I spent much of this week at KM World 2014 in Washington, DC and the past few days I was working on notes and blog posts for here, but time to get them in readable form and posted wasn’t quite there, so today they became a Personal InfoCloud post, KM World 2014 is a Real Gem.
I had a great time with fantastic people whom I’ve known and people new to me. I spent a lot of time talking about work projects and being back on the consulting side again, but also getting content out and what makes sense with prioritization. I had a lot of great meetings and less formal chats about the state of things as well as trying out some metaphors for framing some things to gage how well they hold up.
I have a lot of snippets to explore and post that have come out of this past week, but I’m digging out of email, notes, snippets, and other things tucked away from this past week.
Catching Up On Personal InfoCloud Blog Posts
Things here are a little quiet as I have been in writing mode as well as pitching new work. I have been blogging work related items over at Personal InfoCloud, but I am likely only going to be posting summaries of those pieces here from now on, rather than the full posts. I am doing this to concentrate work related posts, particularly on a platform that has commenting available. I am still running my own blogging tool here at vanderwal.net I wrote in 2001 and turned off the comments in 2006 after growing tired of dealing comment spam.
The following are recently posted over at Personal InfoCloud
SharePoint 2007: Gateway Drug to Enterprise Social Tools
SharePoint 2007: Gateway Drug to Enterprise Social Tools focusses on the myriad of discussions I have had with clients of mine, potential clients, and others from organizations sharing their views and frustrations with Microsoft SharePoint as a means to bring solid social software into the workplace. This post has been brewing for about two years and is now finally posted.
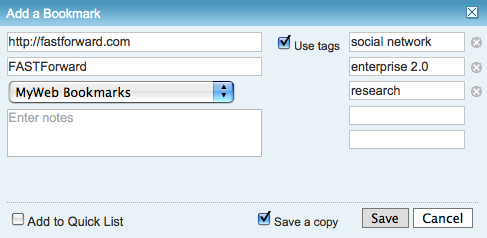
Optimizing Tagging UI for People & Search
Optimizing Tagging UI for People and Search focuses on the lessons learned and usability research myself and others have done on the various input interfaces for tagging, particularly tagging with using multi-term tags (tags with more than one word). The popular tools have inhibited adoption of tagging with poor tagging interaction design and poor patterns for humans entering tags that make sense to themselves as humans.
LinkedIn: Social Interaction Design Lessons Learned (not to follow)
I have a two part post on LinkedIn's social interaction design. LinkedIn: Social Interaction Design Lessons Learned (not to follow) - 1 of 2 looks at what LinkedIn has done well in the past and had built on top. Many people have expressed the new social interactions on LinkedIn have decreased the value of the service for them.
The second part, LinkedIn: Social Interaction Design Lessons Learned (not to follow) - 2 of 2 looks at the social interaction that has been added to LinkedIn in the last 18 months or so and what lessons have we as users of the service who pay attention to social interaction design have learned. This piece also list ways forward from what is in place currently.
Optimizing Tagging UI for People & Search
Overview/Intro
One of my areas of focus is around social tools in the workplace (enterprise 2.0) is social bookmarking. Sadly, is does not have the reach it should as it and wiki (most enterprise focused wikis have collective voice pages (blogs) included now & enterprise blog tools have collaborative document pages (wikis). I focus a lot of my attention these days on what happens inside the organizationís firewall, as that is where their is incredible untapped potential for these tools to make a huge difference.
One of the things I see on a regular basis is tagging interfaces on a wide variety of social tools, not just in social bookmarking. This is good, but also problematic as it leads to a need for a central tagging repository (more on this in a later piece). It is good as emergent and connective tag terms can be used to link items across tools and services, but that requires consistency and identity (identity is a must for tagging on any platform and it is left out of many tagging instances. This greatly decreases the value of tagging - this is also for another piece). There are differences across tools and services, which leads to problems of use and adoption within tools is tagging user interface (UI).
Multi-term Tag Intro
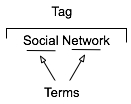 The multi-term tag is one of the more helpful elements in tagging as it provides the capability to use related terms. These multi-term tags provide depth to understanding when keeping the related tag terms together. But the interfaces for doing this are more complex and confusing than they should be for human, as well as machine consumption.
The multi-term tag is one of the more helpful elements in tagging as it provides the capability to use related terms. These multi-term tags provide depth to understanding when keeping the related tag terms together. But the interfaces for doing this are more complex and confusing than they should be for human, as well as machine consumption.
In the instance illustrated to the tag is comprised or two related terms: social and network. When the tool references the tag, it is looking at both parts as a tag set, which has a distinct meaning. The individual terms can be easily used for searches seeking either of those terms, but knowing the composition of the set, it is relatively easy for the service to offer up "social network" when a person seeks just social or network in a search query.
One common hindrance with social bookmarking adoption is those familiar with it and fans of it for enterprise use point to Delicious, which has a couple huge drawbacks. The compound multi-term tag or disconnected multi-term tags is a deep drawback for most regular potential users (the second is lack of privacy for shared group items). Delicious breaks a basic construct in user focussed design: Tools should embrace human methods of interaction and not humans embracing tech constraints. Delicious is quite popular with those of us malleable in our approach to adopt a technology where we adapt our approach, but that percentage of potential people using the tools is quite thin as a percentage of the population.. Testing this concept takes very little time to prove.
So, what are the options? Glad you asked. But, first a quick additional excursion into why this matters.
Conceptual Models Missing in Social Tool Adoption
One common hinderance for social tool adoption is most people intended to use the tools are missing the conceptual model for what these tools do, the value they offer, and how to personally benefit from these values. There are even change costs involved in moving from a tool that may not work for someone to something that has potential for drastically improved value. The "what it does", "what value it has", and "what situations" are high enough hurdles to cross, but they can be done with some ease by people who have deep knowledge of how to bridge these conceptual model gaps.
What the tools must not do is increase hurdles for adoption by introducing foreign conceptual models into the understanding process. The Delicious model of multi-term tagging adds a very large conceptual barrier for many & it become problematic for even considering adoption. Optimally, Delicious should not be used alone as a means to introduce social bookmarking or tagging.
We must remove the barriers to entry to these powerful offerings as much as we can as designers and developers. We know the value, we know the future, but we need to extend this. It must be done now, as later is too late and these tools will be written off as just as complex and cumbersome as their predecessors.
If you are a buyer of these tools and services, this is you guideline for the minimum of what you should accept. There is much you should not accept. On this front, you need to push back. It is your money you are spending on the products, implementation, and people helping encourage adoption. Not pushing back on what is not acceptable will greatly hinder adoption and increase the costs for more people to ease the change and adoption processes. Both of these costs should not be acceptable to you.
Multi-term Tag UI Options
Compound Terms
I am starting with what we know to be problematic for broad adoption for input. But, compound terms also create problems for search as well as click retrieval. There are two UI interaction patterns that happen with compound multi-term tags. The first is the terms are mashed together as a compound single word, as shown in this example from Delicious.
The problem here is the mashing the string of terms "architecture is politics" into one compound term "architectureispolitics". Outside of Germanic languages this is problematic and the compound term makes a quick scan of the terms by a person far more difficult. But it also complicates search as the terms need to be broken down to even have LIKE SQL search options work optimally. The biggest problem is for humans, as this is not natural in most language contexts. A look at misunderstood URLs makes the point easier to understand (Top Ten Worst URLs)
The second is an emergent model for compound multi-term tags is using a term delimiter. These delimiters are often underlines ( _ ), dots ( . ), or hyphens ( - ). A multi-term tag such as "enterprise search" becomes "enterprise.search", "enterprise_search" and "enterprise-search".
While these help visually they are less than optimal for reading. But, algorithmically this initially looks to be a simple solution, but it becomes more problematic. Some tools and services try to normalize the terms to identify similar and relevant items, which requires a little bit of work. The terms can be separated at their delimiters and used as properly separated terms, but since the systems are compound term centric more often than not the terms are compressed and have similar problems to the other approach.
Another reason this is problematic is term delimiters can often have semantic relevance for tribal differentiation. This first surface terms when talking to social computing researchers using Delicious a few years ago. They pointed out that social.network, social_network, and social-network had quite different communities using the tags and often did not agree on underlying foundations for what the term meant. The people in the various communities self identified and stuck to their tribes use of the term differentiated by delimiter.
The discovery that these variations were not fungible was an eye opener and quickly had me looking at other similar situations. I found this was not a one-off situation, but one with a fair amount of occurrence. When removing the delimiters between the terms the technologies removed the capability of understanding human variance and tribes. This method also breaks recommendation systems badly as well as hindering the capability of augmenting serendipity.
So how do these tribes identify without these markers? Often they use additional tags to identity. The social computing researchers add "social computing", marketing types add "marketing", etc. The tools then use their filtering by co-occurrence of tags to surface relevant information (yes, the ability to use co-occurrence is another tool essential). This additional tag addition help improve the service on the whole with disambiguation.
Disconnected Multi-term Tags
The use of distinct and disconnected term tags is often the intent for space delimited sites like Delicious, but the emergent approach of mashing terms together out of need surfaced. Delicious did not intend to create mashed terms or delimited terms, Joshua Schachter created a great tool and the community adapted it to their needs. Tagging services are not new, as they have been around for more than two decades already, but how they are built, used, and platforms are quite different now. The common web interface for tagging has been single terms as tags with many tags applied to an object. What made folksonomy different from previous tagging was the inclusion of identity and a collective (not collaborative) voice that intelligent semantics can be applied to.
The downside of disconnected terms in tagging is certainty of relevance between the terms, which leads to ambiguity. This discussion has been going on for more than a decade and builds upon semantic understanding in natural language processing. Did the tagger intend for a relationship between social & network or not. Tags out of the context of natural language constructs provide difficulties without some other construct for sense making around them. Additionally, the computational power needed to parse and pair potential relevant pairings is somethings that becomes prohibitive at scale.
Quoted Multi-term Tags
One of the methods that surfaced early in tagging interfaces was the quoted multi-term tags. This takes becomes #&039;research "social network" blog' so that the terms social network are bound together in the tool as one tag. The biggest problem is still on the human input side of things as this is yet again not a natural language construct. Systematically the downside is these break along single terms with quotes in many of the systems that have employed this method.
What begins with a simple helpful prompt...:
Still often can end up breaking as follows (from SlideShare):
Comma Delimited Tags
Non-space delimiters between tags allows for multi-term tags to exist and with relative ease. Well, that is relative ease for those writing Western European languages that commonly use commas as a string separator. This method allows the system to grasp there are multi-term tags and the humans can input the information in a format that may be natural for them. Using natural language constructs helps provide the ability ease of adoption. It also helps provide a solid base for building a synonym repository in and/or around the tagging tools.
While this is not optimal for all people because of variance in language constructs globally, it is a method that works well for a quasi-homogeneous population of people tagging. This also takes out much of the ambiguity computationally for information retrieval, which lowers computational resources needed for discernment.
Text Box Per Tag
Lastly, the option for input is the text box per tag. This allows for multi-term tags in one text box. Using the tab button on the keyboard after entering a tag the person using this interface will jump down to the next empty text box and have the ability to input a term. I first started seeing this a few years ago in tagging interfaces tools developed in Central Europe and Asia. The Yahoo! Bookmarks 2 UI adopted this in a slightly different implementation than I had seen before, but works much the same (it is shown here).
There are many variations of this type of interface surfacing and are having rather good adoption rates with people unfamiliar to tagging. This approach tied to facets has been deployed in Knowledge Plaza by Whatever s/a and works wonderfully.
All of the benefits of comma delimited multi-term tag interfaces apply, but with the added benefit of having this interface work internationally. International usage not only helps build synonym resources but eases language translation as well, which is particularly helpful for capturing international variance on business or emergent terms.
Summary
This content has come from more than four years of research and discussions with people using tools, both inside enterprise and using consumer web tools. As enterprise moves more quickly toward more cost effective tools for capturing and connecting information, they are aware of not only the value of social tools, but tools that get out the way and allow humans to capture, share, and interact in a manner that is as natural as possible with the tools getting smart, not humans having to adopt technology patterns.
This is a syndicated version of the same post at Optimizing Tagging UI for People & Search :: Personal InfoCloud that has moderated comments available.
Tale of Two Tunnels: Web 2.0 and Enterprise 2.0
Yesterday I made a few comments in Twitter that prompted a fair amount of questions and requests for more information. The quips I made were about the differences between Web 2.0 (yes, an ambiguous term) and Enterprise 2.0 (equally ambiguous term both for the definition of enterprise and the 2.0 bit). My comments were in response to Bruce Stewart's comment The whole "Enterprise 2.0" schtick is wearing thin, unless you've been monitoring real results. Otherwise you're just pumping technology.. In part I agree, but I am really seeing things still are really early in the emergence cycle and there is still much need for understanding of the social tools and the need for them, as well as how they fit in. There are many that are selling the tools as technologies with great promise. We have seen the magic pill continually pitched and bought through out the history of business tools. (For those new to the game or only been paying attention for the last 15 years, a huge hint, THERE IS NO MAGIC PILL).
Tale of 2 Tunnels
One comment I made yesterday is, "the difference between Web 2.0 and Enterprise 2.0 is like the difference building a tunnel through rock and tunnel under water".
That this is getting at is Web 2.0 takes work to build to get through the earth, but once built it can suffer from imperfections and still work well. The tunnel can crack and crumble a little, but still get used with diminished capacity. We can look at Facebook, which has a rather poor interface and still gets used. Twitter is another example of a Web 2.0 solution that has its structural deficiencies and outages, but it still used as well as still loved (their Fail Whale is on a t-shirt now and a badge of pride worn by loyal users).
The Enterprise 2.0 tunnel is built under water. This takes more engineering understanding, but it also requires more fault testing and assurances. A crack or crumbling of a tool inside an organization is not seen kindly and raises doubts around the viability of the tool. The shear volume of users inside an organization using these tools is orders of magnitude less than in the open consumer web world, but faults are more deadly.
The other important factor is perceived fear of the environment. Fewer people (by pure numbers - as the percentages are likely the same, more on this later) are fearful of tunnels through land, they may not have full faith in them, but they know that they will likely make it safely on all of their journeys. The tunnels under water have greater fears as one little crack can cause flooding and drowning quickly. Fears of use of social tools inside an organization is often quite similar, there may be many that are not fearful, but if you spend time talking to people in organizations not using tools (it is the majority at this point) they are fearful of open sharing as that could lead to trouble. People are not comfortable with the concept as they are foreign to it as they are lacking the conceptual models to let them think through it.
Enterprise 2.0 is not Web 2.0
Another statement yesterday that garnered a lot of feedback was, "Web 2.0 does not work well in enterprise, but the approaches and understandings of Web 2.0 modified for enterprise work really well." The web is not enterprise or smaller organizations for that matter. The open consumer web has different scale and needs than inside organizations and through their firewalls. A small percentage of people using the web can get an account on a tool have have appear to be wildly successful correctly claiming 70 million or 100 million people are or have used their tool. But, even 100 million people is a small percentage of people using the web. Looking at real usage and needs for those tools the numbers are really smaller. Most darlings of the Web 2.0 phase have fewer than 10 million users, which is about 5% of the open consumer web users in the United States. On the web a start-up is seen as successful with 500,000 users after a year or two and is likely to have the capability to be self sufficient at that level too. Granted there are many players in the same market niches on the web and the overall usage for link sharing and recommending for Digg, Mixx, or Reddit is much higher across the sum of these tools than in just one of these tools (obviously).
These percentages of adoption and use inside organizations can make executives nervous that their money is not reaching as many employees as they wish. The percentages that can be similar to the web's percentages of high single digit adoption rates to the teens is seen as something that really needs more thinking and consideration.
Enterprise 2.0 is more than just tools (see my Enterprise Social Tools: Components for Success for better understanding) as it also includes interface/interaction design for ease of use, sociality, and encouragement of use. The two biggest factors that are needed inside an organization that can receive less attention on the web are the sociality and encouragement of use.
Understanding sociality is incredibly important inside an organization as people are used to working in groups (often vertical in their hierarchy) that have been dictated to them for use. When the walls are broken down and people are self-finding others with similar interests and working horizontally and diagonally connecting and sharing with others and consuming the collective flows of information their comfortable walls of understanding are gone. A presentation in Copenhagen at Reboot on Freely Seeping Through the Walls of the Garden focussed just on this issue. This fear inside the enterprise is real. Much of the fear is driven by lacking conceptual models and understanding the value they will derive from using the tools and services. People need to know who the other people are that they are sharing with and what their motivations are (to some degree) before they have comfort in sharing themselves.
Encouraging use is also central to increased adoption inside organizations. Many organizations initial believe that Web 2.0 tools will take off and have great adoption inside an organization. But, this is not a "build it and they will come" scenario, even for the younger workers who are believed to love these tools and services and will not stay in a company that does not have them. The reality is the tools need selling their use, value derived from them, the conceptual models around what they do, and easing fears. Adoption rates grow far beyond the teen percentages in organizations that take time guiding people about the use of the tools and services. Those organizations that take the opportunity to continually sell the value and use for these tools they have in place get much higher adoption and continued engagement with the tools than those who do nothing and see what happens.
Gaps in Enterprise Tools
The last related statement was around the gaps in current and traditional enterprise tools. At the fantastic Jive Enterprise UI Summit in Aspen a few weeks ago there was a lot of discussion about enterprise tools, their UI, and ease of use for employees by the incredible collection of people at the event. One of the things that was shown was a killer path of use through a wide encompassing enterprise toolset that was well designed and presented by SAP's Dan Rosenberg who has done an incredible job of putting user experience and thinking through the needed workflows and uses of enterprise tools at the forefront of enterprise software planning. Given the excellent design and incredible amount of user experience thought that went into the tools behind the SAP toolset in the scenario (one of the best I have seen - functioning or blue sky demoed) there are still gaps. Part of this is identifying of gaps comes from traditional business thinking around formal processes and the tools ensure process adherence. But, the reality is the tools are quite often inflexible (I am not talking about SAP tools, but traditional enterprise tools in general), the cost of time and effort is beyond the gain for individuals to document and annotate all decisions and steps along the way. The hurdles to capture information and share it are often too large for capturing one to 10 quick sentences of information that can be retained for one's own benefit or shared with other where it is relevant.
There is another gap in business around the collective intelligence that is needed, which can lead to collaboration. Most businesses and their tools focus on collaboration and set groups, but at the same time wonder why they do not know what their company knows and knowledge is not all being captured. First there is a difference between collective and collaborative activities and the tools and design around and for those different activities is more than a nuance of semantics it is a huge barrier to capturing, sharing, and learning from information that leads to knowledge if it is not understood well. Enterprise has gone through its phases of knowledge management tools, from forms for capturing information, forums for sharing, and up to enterprise content management systems (ECM) that encompass document management, content management, knowledge management, and information harvesting. But, the gaps still exist.
These existing gaps are around conversations not being captured (the walls of the halls have no memory (well today they do not)) and increasingly the ubiquitous communication channel in organizations, e-mail, is being worked around. Quick decisions are not being documented as it is not enough for a document or worth completing a form. As the iterative processes of development, design, and solution engineering are happening at quicker and smaller increments the intelligence behind the decisions is not being captured or shared. This is largely because of the tools.
As has always been the case large enterprise systems are worked around through the use of smaller and more nimble solutions that augment the existing tools. Even in Dan's incredible demo I saw gaps for these tools. The quick tools that can fill these gaps are blogs, wikis, social bookmarking, tagging, Twitter type sharing, Veodia type video sharing, instant messaging, etc. There are many avenues to quickly capture information and understanding and share it. These tools get out of the way and allow what is in someone's head to get digitized and later structured by the individual themselves or other people whom have had the information shared with them in a community space. This turns into flows through streams that can be put into many contexts and needs as well as reused as needed.
Another point Dan stated at the Enterprise UI Summit that is dead on, is organizations are moving out of the vertical structures and moving to the horizontal. This is having a profound effect on the next generation of business tools and processes. This is also an area for Enterprise 2.0 tools as they easily open up the horizontal and diagonal prospects and tie into it the capability for easily understanding who these newly found people are in an organization through looking at their profiles, which eases their fears around sharing and unfamiliar environments as well as their related tasks.
[Comments are open and moderated at Tale of Two Tunnels: Web 2.0 and Enterprise 2.0 :: Personal InfoCloud]
Stewart Mader is Now Solo and One to Watch and Hire
There seems to be many people that are joining the ranks of solo service providers around social tools. Fortunately there are some that are insanely great people taking these steps. Stewart Mader is one of these insanely great people now fully out on his own. Stewart Mader's Wiki Adoption Services are the place to start for not only initial stages of thinking through and planning successful wiki projects, but also for working through the different needs and perspectives that come with the 6 month and one year realizations.
Those of you not familiar with Stewart, he wrote the best book on understanding wikis and adoption, Wikipatterns and is my personal favorite speaker on the subject of wikis. Others may have more broadly known names, but can not come close to touching his breadth nor depth of knowledge on the subject. His understandings of wikis and their intersection with other forms and types of social tools is unsurpassed.
I welcome Stewart to the realm of social tool soloists experts. I look forward to one day working on a project with Stewart.
Speaking at the International Forum on Enterprise 2.0 Near Milan, Italy
Under a month from now I have the wonderful pleasure of speaking at the International Forum on Enterprise 2.0, this is just outside of Milan in Varese, Italy on June 25, 2008. I am really looking forward to this event as there are many people whom I chat with on Skype with and chat with in other ways about enterprise and the use of social tools inside these organizations. It is a wonderful opportunity to meet them in person and to listen to them live as they present. Already I know many people attending the event from the United Kingdom, Switzerland, Germany, Austria, Spain, and (of course) Italy. If you are in Europe and have interest this should be a great event to get a good overview and talk with others with interest and experience. Oh, did I mention the conference is FREE?
I will be presenting an overview on social bookmarking and folksonomy and the values that come out of these tools, but also the understanding needed to make good early decisions about the way forward.
I look forward to meeting those of you who attend.
Enterprise 2.0 Boston - After Noah: What to do After the Flood (of Information)
I am looking forward to being at the Enterprise 2.0 Conference in Boston from June 10 to June 12, 2008. I am going to be presenting on June 10, 2008 at 1pm on After Noah: Making Sense of the Flood (of Information). This presentation looks at what to expect with social bookmarking tools inside an organization as they scale and mature. It also looks at how to manage the growth as well as encourage the growth.
Last year at the same Enterprise 2.0 conference I presented on Bottom-up Tagging (the presentation is found at Slideshare, Bottom-up All the Way Down: How Tags Help Businesses Organize, which has had over 8,800 viewing on Slideshare), which was more of a foundation presentation, but many in the audience were already running social bookmarking services in-house or trying them in some manner. This year my presentation is for those with an understanding of what social bookmarking and folksonomy are and are looking for what to expect and how to manage what is happening or will be coming along. I will be covering how to manage heavy growth as well as how to increase adoption so there is heavy usage to manage.
I look forward to seeing you there. Please say hello, if you get a chance.
Enterprise Social Tools: Components for Success
One of the things I continually run across talking with organizations deploying social tools inside their organization is the difficultly getting all the components to mesh. Nearly everybody is having or had a tough time with getting employees and partners to engage with the services, but everybody is finding out it is much more than just the tools that are needed to consider. The tools provide the foundation, but once service types and features are sorted out, it get much tougher. I get frustrated (as do many organizations whom I talk with lately) that social tools and services that make up enterprise 2.0, or whatever people want to call it, are far from the end of the need for getting it right. There is great value in these tools and the cost of the tools is much less than previous generations of enterprise (large organization) offerings.
Social tools require much more than just the tools for their implementation to be successful. Tool selection is tough as no tool is doing everything well and they all are focussing on niche areas. But, as difficult as the tool selection can be, there are three more elements that make up what the a successful deployment of the tools and can be considered part of the tools.
Four Rings of Enterprise Social Tools
 The four elements really have to work together to make for a successful services that people will use and continue to use over time. Yes, I am using a venn diagram for the four rings as it helps point out the overlaps and gaps where the implementations can fall short. The overlaps in the diagram is where the interesting things are happening. A year ago I was running into organizations with self proclaimed success with deployments of social tools (blogs, wikis, social bookmarking, forums, etc.), but as the desire for more than a simple set of blogs (or whichever tool or set of tools was selected) in-house there is a desire for greater use beyond some internal early adopters. This requires paying close attention to the four rings.
The four elements really have to work together to make for a successful services that people will use and continue to use over time. Yes, I am using a venn diagram for the four rings as it helps point out the overlaps and gaps where the implementations can fall short. The overlaps in the diagram is where the interesting things are happening. A year ago I was running into organizations with self proclaimed success with deployments of social tools (blogs, wikis, social bookmarking, forums, etc.), but as the desire for more than a simple set of blogs (or whichever tool or set of tools was selected) in-house there is a desire for greater use beyond some internal early adopters. This requires paying close attention to the four rings.
Tools
The first ring is rather obvious, it is the tools. The tools come down to functionality and features that are offered, how they are run (OS, rack mount, other software needed, skills needed to keep them running, etc.), how the tools are integrated into the organization (authentication, back-up, etc.), external data services, and the rest of the the usual IT department checklist. The tools get a lot of attention from many analysts and tech evangelists. There is an incredible amount of attention on widgets, feeds, APIs, and elements for user generated contribution. But, the tools do not get you all of the way to a successful implementation. The tools are not a mix and match proposition.
Interface & Ease of Use
One thing that the social software tools from the consumer web have brought is ease of use and simple to understand interfaces. The tools basically get out of the way and bring in more advanced features and functionality as needed. The interface also needs to conform to expectations and understandings inside an organization to handle the flow of interaction. What works for one organization may be difficult for another organization, largely due to the tools and training, and exposure to services outside their organization. Many traditional enterprise tools have been trying to improve the usability and ease of use for their tools over the last 4 to 5 years or so, but those efforts still require massive training and large binders that walk people through the tools. If the people using the tools (not administering the tools need massive amounts of training or large binders for social software the wrong tool has been purchased).
Sociality
Sociality is the area where people manage their sharing of information and their connections to others. Many people make the assumption that social tools focus on everything being shared with everybody, but that is not the reality in organizations. Most organizations have tight boundaries on who can share what with whom, but most of those boundaries get in the way. One of the things I do to help organizations is help them realize what really needs to be private and not shared is often much less than what they regulate. Most people are not really comfortable sharing information with people they do not know, so having comfortable spaces for people to share things is important, but these spaces need to have permeable walls that encourage sharing and opening up when people are sure they are correct with their findings.
Sociality also includes the selective groups people belong to in organizations for project work, research, support, etc. that are normal inside organizations to optimize efficiency. But, where things get really difficult is when groups are working on similar tasks that will benefit from horizontal connections and sharing of information. This horizontal sharing (as well as diagonal sharing) is where the real power of social tools come into play as the vertical channels of traditional organization structures largely serve to make organizations inefficient and lacking intelligence. The real challenge for the tools is the capability to surface the information of relevance from selective groups to other selective groups (or share information more easily out) along the way. Most tools are not to this point yet, largely because customers have not been asking for this (it is a need that comes from use over time) and it can be a difficult problem to solve.
One prime ingredient for social tool use by people is providing a focus on the people using the tools and their needs for managing the information they share and the information from others that flow through the tool. Far too often the tools focus on the value the user generated content has on the system and information, which lacks the focus of why people use the tools over time. People use tools that provide value to them. The personal sociality elements of whom are they following and sharing things with, managing all contributions and activities they personally made in a tool, ease of tracking information they have interest in, and making modifications are all valuable elements for the tools to incorporate. The social tools are not in place just to serve the organization, they must also serve the people using the tools if adoption and long term use important.
Encouraging Use
Encouraging use and engagement with the tools is an area that all organizations find they have a need for at some point and time. Use of these tools and engagement by people in an organization often does not happen easily. Why? Normally, most of the people in the organization do not have a conceptual framework for what the tools do and the value the individuals will derive. The value they people using the tools will derive needs to be brought to the forefront. People also usually need to have it explained that the tools are as simple as they seem. People also need to be reassured that their voice matters and they are encouraged to share what they know (problems, solutions, and observations).
While the egregious actions that happen out on the open web are very rare inside an organization (transparency of who a person is keeps this from happening) there is a need for a community manager and social tool leader. This role highlights how the tools can be used. They are there to help people find value in the tools and provide comfort around understanding how the information is used and how sharing with others is beneficial. Encouraging use takes understanding the tools, interface, sociality, and the organization with its traditions and ways of working.
The Overlaps
The overlaps in the graphic are where things really start to surface with the value and the need for a holistic view. Where two rings over lap the value is easy to see, but where three rings overlap the missing element or element that is deficient is easier to understand its value.
Tools and Interface
Traditional enterprise offerings have focussed on the tools and interface through usability and personalization. But the tools have always been cumbersome and the interfaces are not easy to use. The combination of the tools and interface are the core capabilities that traditionally get considered. The interface is often quite flexible for modification to meet an organizations needs and desires, but the capabilities for the interface need to be there to be flexible. The interface design and interaction needs people who have depth in understanding the broad social and information needs the new tools require, which is going to be different than the consumer web offerings (many of them are not well thought through and do not warrant copying).
Tools and Sociality
Intelligence and business needs are what surface out of the tools capabilities and sociality. Having proper sociality that provides personal tools for managing information flows and sharing with groups as well as everybody as it makes sense to an individual is important. Opening up the sharing as early as possible will help an organization get smarter about itself and within itself. Sociality also include personal use and information management, which far few tools consider. This overlap of tools and sociality is where many tools are needing improvement today.
Interface and Encouraging Use
Good interfaces with easy interaction and general ease of use as well as support for encouraging use are where expanding use of the tools takes place, which in turn improves the return on investment. The ease of use and simple interfaces on combined with guidance that provides conceptual understanding of what these tools do as well as providing understanding that eases fears around using the tools (often people are fearful that what they share will be used against them or their job will go away because they shared what they know, rather than they become more valuable to an organization by sharing as they exhibit expertise). Many people are also unsure of tools that are not overly cumbersome and that get out of the way of putting information in to the tools. This needs explanation and encouragement, which is different than in-depth training sessions.
Sociality and Encouraging Use
The real advantages of social tools come from the combination of getting sociality and encouraging use correct. The sociality component provides the means to interact (or not) as needed. This is provided by the capabilities of the product or products used. This coupled with a person or persons encouraging use that show the value, take away the fears, and provide a common framework for people to think about and use the tools is where social comfort is created. From social comfort people come to rely on the tools and services more as a means to share, connect, and engage with the organization as a whole. The richness of the tools is enabled when these two elements are done well.
The Missing Piece in Overlaps
This section focusses on the graphic and the three-way overlaps (listed by letter: A; B; C; and D). The element missing in the overlap or where that element is deficient is the focus.
Overlap A
This overlap has sociality missing. When the tool, interface, and engagement are solid, but sociality is not done well for an organization there may be strong initial use, but use will often stagnate. This happens because the sharing is not done in a manner that provides comfort or the services are missing a personal management space to hold on to a person's own actions. Tracking one's own actions and the relevant activities of others around the personal actions is essential to engaging socially with the tools, people, and organization. Providing comfortable spaces to work with others is essential. One element of comfort is built from know who the others are whom people are working with, see Elements of Social Software and Selective Sociality and Social Villages (particularly the build order of social software elements) to understand the importance.
Overlap B
This overlap has tools missing, but has sociality, interface, and encouraging use done well. The tools can be deficient as they may not provide needed functionality, features, or may not scale as needed. Often organizations can grow out of a tool as their needs expand or change as people use the tools need more functionality. I have talked with a few organizations that have used tools that provide simple functionality as blogs, wikis, or social bookmarking tools find that as the use of the tools grows the tools do not keep up with the needs. At times the tools have to be heavily modified to provide functionality or additional elements are needed from a different type of tool.
Overlap C
Interface and ease of use is missing, while sociality, tool, and encouraging use are covered well. This is an area where traditional enterprise tools have problems or tools that are built internally often stumble. This scenario often leads to a lot more training or encouraging use. Another downfall is enterprise tools are focussed on having their tools look and interact like consumer social web tools, which often are lacking in solid interaction design and user testing. The use of social tools in-house will often not have broad use of these consumer services so the normal conventions are not understood or are not comfortable. Often the interfaces inside organizations will need to be tested and there many need to be more than one interface and feature set provided for depth of use and match to use perceptions.
Also, what works for one organization, subset of an organization, or reviewer/analyst will not work for others. The understanding of an organization along with user testing and evaluation with a cross section of real people will provide the best understanding of compatibility with interface. Interfaces can also take time to take hold and makes sense. Interfaces that focus on ease of use with more advanced capabilities with in reach, as well as being easily modified for look and interactions that are familiar to an organization can help resolve this.
Overlap D
Encouraging use and providing people to help ease people's engagement is missing in many organizations. This is a task that is often overlooked. The tools, interface, and proper sociality can all be in place, but not having people to help provide a framework to show the value people get from using the tools, easing concerns, giving examples of uses for different roles and needs, and continually showing people success others in an organization have with the social tool offerings is where many organization find they get stuck. The early adopters in an organization may use the tools as will those with some familiarity with the consumer web social services, but that is often a small percentage of an organization.
Summary
All of this is still emergent and early, but these trends and highlights are things I am finding common. The two areas that are toughest to get things right are sociality and encouraging use. Sociality is largely dependent on the tools, finding the limitations in the tools takes a fair amount of testing often to find limitations. Encouraging use is more difficult at the moment as there are relatively few people who understand the tools and the context that organizations bring to the tools, which is quite different from the context of the consumer social web tools. I personally only know of a handful or so of people who really grasp this well enough to be hired. Knowing the "it depends moments" is essential and knowing that use is granular as are the needs of the people in the organization. Often there are more than 10 different use personas if not more that are needed for evaluating tools, interface, sociality, and encouraging use (in some organizations it can be over 20). The tools can be simple, but getting this mix right is not simple, yet.
[Comments are open and moderated at Enterprise Social Tools: Components for Success :: Personal InfoCloud
Getting Info into the Field with Extension
This week I was down in Raleigh, North Carolina to speak at National Extension Technology Conference (NETC) 2008, which is for the people running the web and technology components for what used to be the agricultural extension of state universities, but now includes much more. This was a great conference to connect with people trying to bring education, information, and knowledge services to all communities, including those in rural areas where only have dial-up connectivity to get internet access. The subject matter presented is very familiar to many other conferences I attend and present at, but with a slightly different twist, they focus on ease of use and access to information for everybody and not just the relatively early adopters. The real values of light easy to use interfaces that are clear to understand, well structured, easy to load, and include affordance in the initial design consideration is essential.
I sat in on a few sessions, so to help tie my presentation to the audience, but also listen to interest and problems as they compare to the organizations I normally talk to and work with (mid-size member organizations up to very large global enterprise). I sat in on a MOSS discussion. This discussion about Sharepoint was indiscernible from any other type of organization around getting it to work well, licensing, and really clumsy as well as restrictive sociality. The discussion about the templates for different types of interface (blogs and wikis) were the same as they they do not really do or act like the template names. The group seemed to have less frustration with the wiki template, although admitted it was far less than perfect, it did work to some degree with the blog template was a failure (I normally hear both are less than useful and only resemble the tools in name not use). [This still has me thinking Sharepoint is like the entry drug for social software in organizations, it looks and sounds right and cool, but is lacking the desired kick.]
I also sat down with the project leads and developers of an eXtension wide tool that is really interesting to me. It serves the eXtension community and they are really uncoupling the guts of the web tools to ease greater access to relevant information. This flattening of the structures and new ways of accessing information is already proving beneficial to them, but it also has brought up the potential to improve ease some of the transition for those new to the tools. I was able to provide feedback that should provide a good next step. I am looking forward to see that tool and the feedback in the next three to six months as it has incredible potential to ease information use into the hands that really need it. It will also be a good example for how other organizations can benefit from similar approaches.
Comments are open (with usual moderation) at this post at Getting Info into the Field with Extension :: Personal InfoCloud.
YouTube New Interface and Social Interaction Design Santiy Check
YouTube has released a new design for the site and its individual video pages. This gets shared in Google Operating System :: User Inferface Updates at YouTube and TechCrunch :: YouTube Updates Layout, Now with Tabs and Statistics. While the new design looks nice and clean, it has one design bug that is horribly annoying it has mixed interaction design metaphors for its tabs or buttons.
Broken Interaction Design on Buttons or Tabs
 As the image shows the Share, Favorite, Playlists, and Flag buttons or tabs all have similar design treatment, but they do not have the same actions when you click on them. Three of the items (Share, Playlists, and Flag) all act as tabs that open up a larger area below them to provide more options and information. But, the Favorites acts like a button that when clicked it marks the item as a favorite.
As the image shows the Share, Favorite, Playlists, and Flag buttons or tabs all have similar design treatment, but they do not have the same actions when you click on them. Three of the items (Share, Playlists, and Flag) all act as tabs that open up a larger area below them to provide more options and information. But, the Favorites acts like a button that when clicked it marks the item as a favorite.
This is incredibly poor interaction design as all the items should act in the same manner. If the items do not have the same action properties they really should not look the same and be in the same action space. Favorites should be a check box or a binary interface for on and off. That interaction patter more closely matches the Rate section and seems like it should have been there rather than showing a lack of understanding interaction design basics and confusing people using the site/service.
Social Sites Seem to Share a Lack of Interaction Understanding
This should have been a no brainer observation for a design manager or somebody with a design sanity check. YouTube is far from the the only site/service doing this. Nearly all of the services are not grasping the basics or are broadly applying design patterns to all user scenarios when they really do not fit all scenarios and user types (nearly every service I talk to know exactly the use type a person fits into but never takes this into account in optimization of design patterns that match that use need). Facebook really falls into this hole badly and never seems to grasp they are really making a mess of things the more features and functionality they are bringing into their service without accounting for the design needs in the interface.
My seemingly favorite site to nit pick is LinkedIn which I use a lot and has been a favorite, but their social interaction additions and interactive interfaces really need much better sanity checks and testing before they go into production (even into the beta interface). LinkedIn is really trying to move forward and they are moving in the right direction, but they really need better design thinking with their new features and functionality. Their new design is ready to handle some of the new features, but the features need a lot more refining. The new design shows they have a really good grasp that the interface needs to be a flexible foundation to be used as a framework for including new features, which could benefit from treating them as options for personalization. LinkedIn has pulled back many of the social features and seems to be rethinking them and refining them, but they really need some good sanity checks before rolling them out again.
Social Interaction in Enterprise Tools
The befuddled interaction understanding is not germane to commercial or consumer public social web sites, but it also plagues tools aimed at the enterprise. This is not overly surprising as many of the social enterprise (enterprise 2.0) tools and services are copying the public web tools and services to a large degree. This is a good thing, as it puts the focus on ease of use, which has been horribly missing in business focussed tools for far too long. But, the down side for enterprise focussed tools is they are not for the public web they are for business users, who most often do not have familiarity with the conventions on the public web and they have a large cognitive gap in understanding what the tools do and their value. There is less time for playing and testing in most business people's worklife. This means the tools need to get things right up front with clear understanding of the use needs of the people they are building for in business. This seems to be lacking in many tools as there is much copying of poor design that really needs to be tested thoroughly before launching. Business focussed tools are not hitting the same people as are on the web, which will work through poor design and functionality to see what things do. It is also important to consider that there are a wide variety of types of people using these tools with varying needs and varying interaction understandings (this will be another blog post, actually a series of posts that relate to things I have been including in workshops the last six months and presenting the last couple).
[Comments are available and moderated as usual at: YouTube New Interface and Social Interaction Design Santiy Check :: Personal InfoCloud]
Denning and Yaholkovsky on Real Collaboration
The latest edition of the Communications of the ACM (Volume 51, Issue 4 - April 2008) includes an article on Getting to "we", which starts off by pointing out the misuse and mis-understanding of the term collaboration as well as the over use of the practice of collaboration when it is not proper for the need. The authors Peter Denning and Peter Yaholkovsky break down the tools needed for various knowledge needs into four categories: 1) Information sharing; 2) Coordination; 3) Cooperation; and Collaboration. The authors define collaboration as:
Collaboration generally means working together synergistically. If your work requires support and agreement of others before you can take action, you are collaborating.
The article continues on to point out that collaboration is often not the first choice of tools we should reach for, as gathering information, understanding, and working through options is really needed in order to get to the stages of agreement. Their article digs deeply into the resolving "messy problems" through proper collaboration methods. To note, the wiki - the usual darling of collaboration - is included in their "cooperation" examples and not Collaboration. Most of the tools many businesses consider in collaboration tools are in the lowest level, which is "information sharing". But, workflow managment falls into the coordination bucket.
This is one of the better breakdowns of tool sets I have seen. The groupings make a lot of sense and their framing of collaboration to take care of the messiest problems is rather good, but most of the tools and services that are considered to be collaborations tools do not even come close to that description or to the capabilities required.
[Comments are open at Denning and Yaholkovsky on Real Collaboration :: Personal InfoCloud]